Introduction: The new WADA Code 2015
Day 1: The impact of the revised World Anti-Doping Code on the work of National Anti-Doping Agencies
Day 3: Proof of intent (or lack thereof) under the 2015 World Anti-Doping Code
Day 4: Ensuring proportionate sanctions under the 2015 World Anti-Doping Code
Editor's Note
Marjolaine Viret: An attorney-at-law at the Geneva bar, specialising in sports and health law. Her doctoral work in anti-doping was awarded a summa cum laude by the University of Fribourg in early 2015. She gained significant experience in sports arbitration as a senior associate in one of Switzerland’s leading law firms, advising clients, including major sports federations, on all aspects of anti-doping. She also holds positions within committees in sports organisations and has been involved in a variety of roles in the implementation of the 2015 WADC. Her book “Evidence in Anti-Doping at the Intersection of Science & Law” is scheduled for publication in 2015.
Emily Wisnosky: An attorney-at-law admitted to the California bar, she currently participates in the WADC 2015 Commentary research project as a doctoral researcher. She also holds an LLM from the University of Geneva in International Dispute Settlement, with a focus on sports arbitration. Before studying law, she worked as a civil engineer. More...
Introduction: The new WADA Code 2015
Day 2: The “Athlete Patient” and the 2015 World Anti-Doping Code: Competing Under Medical Treatment
Day 3: Proof of intent (or lack thereof) under the 2015 World Anti-Doping Code
Day 4: Ensuring proportionate sanctions under the 2015 World Anti-Doping Code
Editor's note
Herman Ram is the Chief Executive Officer of the Anti-Doping Authority the Netherlands, which is the National Anti-Doping Organization of the country. He has held this position since 2006. After working twelve years as a librarian, Herman Ram started his career in sport management in 1992, when he became Secretary general of the Royal Netherlands Chess Federation. In 1994, he moved on to the same position at the Netherlands Badminton Federation. He was founder and first secretary of the Foundation for the Promotion of Elite Badminton that was instrumental in the advancement of Dutch badminton. In 2000 he was appointed Secretary general of the Netherlands Ski Federation, where he focused, among other things, on the organization of large snowsports events in the Netherlands. Since his appointment as CEO of the Anti-Doping Authority, he has developed a special interest in legal, ethical and managerial aspects of anti-doping policies, on which he has delivered numerous presentations and lectures. On top of that, he acts as Spokesperson for the Doping Authority. Herman Ram holds two Master’s degrees, in Law and in Sport Management. More...
Day 1: The impact of the revised World Anti-Doping Code on the work of National Anti-Doping Agencies
Day 2: The “Athlete Patient” and the 2015 World Anti-Doping Code: Competing Under Medical Treatment
Day 3: Proof of intent (or lack thereof) under the 2015 World Anti-Doping Code
Day 4: Ensuring proportionate sanctions under the 2015 World Anti-Doping Code
On
1 January, a new version of the World Anti-Doping Code (WADC or Code) entered
into force. This blog symposium aims at taking stock of this development and at
offering a preliminary analysis of the key legal changes introduced. The
present blog will put the WADC into a more general historical and political
context. It aims to briefly retrace the emergence of the World Anti-Doping
Agency (WADA) and its Code. It will also reconstruct the legislative process
that led to the adoption of the WADC 2015 and introduce the various
contributions to the blog symposium.More...
Editor's note
Zlatka Koleva is a graduate from the Erasmus University Rotterdam and is currently an Intern at the ASSER International Sports Law Centre.
The decision on appeal in the case
of O’Bannon v. NCAA seems,
at first sight, to deliver answers right on time regarding the unpaid use of
names, images and likenesses (NILs) of amateur college athletes, which has been
an ongoing debate in the US after last year’s district court decision that
amateur players in the college games deserve to receive compensation for their
NILs.[1]
The ongoing struggle for compensation in exchange for NILs used in TV
broadcasts and video games in the US has reached a turning point and many have
waited impatiently for the final say of the Court of Appeal for the 9th
circuit. The court’s ruling on appeal for the 9th circuit, however,
raises more legitimate concerns for amateur sports in general than it offers
consolation to unprofessional college sportsmen. While the appellate court
agreed with the district court that NCAA should provide scholarships amounting
to the full cost of college attendance to student athletes, the former rejected
deferred payment to students of up to 5,000 dollars for NILs rights. The
conclusions reached in the case relate to the central antitrust concerns raised
by NCAA, namely the preservation of consumer demand for amateur sports and how
these interests can be best protected under antitrust law. More...
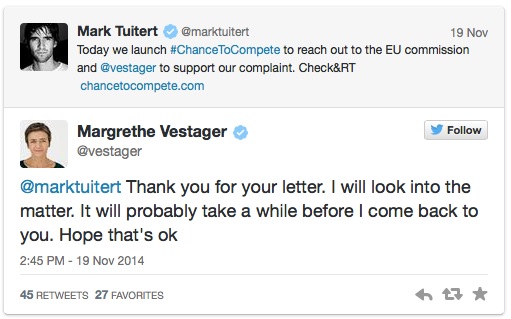
In June 2014, two prominent Dutch speed skaters, Mark Tuitert
(Olympic Champion 1500m) and Niels Kerstholt
(World Champion short track), filed a competition law complaint against the
International Skating Union (ISU) with the European Commission.
ChanceToCompeteTwitter.png (50.4KB)
Today, the
European Commission announced that it has opened a
formal antitrust investigation into International Skating Union (ISU) rules
that permanently ban skaters from competitions such as the Winter Olympics and
the ISU World and European Championships if they take part in events not organised
or promoted by the ISU. The Commissioner for Competition, Margrethe Vestager, stated that the Commission "will
investigate if such rules are being abused to enforce a monopoly over the
organisation of sporting events or otherwise restrict competition. Athletes can
only compete at the highest level for a limited number of years, so there must
be good reasons for preventing them to take part in events."
Since
the case originates from legal advice provided by the ASSER International
Sports Law Centre, we thought it would be helpful to provide some
clarifications on the background of the case and the main legal issues at
stake. More...
Editor’s note
Wil is working as a lawyer since 1980. He
started his legal career at Rechtshulp Rotterdam. Later on he worked for the
Dutch national trade union FNV and law firm Varrolaan Advocaten. Currently he
is participating in the Labour Law Section of lawfirm MHZ-advocaten in Schiedam
in the Netherlands. He is also a member of a joint committee advising the government
in labour issues.
Since 1991 he is dealing with the labour issues
of the trade union for professional football players VVCS and cyclists’ union
VVBW. Since 2002, he works for FIFPro, the worldwide union for professional
football players based in Hoofddorp in the Netherlands. He is involved in many
international football cases and provides legal support for FIFPro members all
over the world. Wil was also involved in the FIFPro Black Book campaign on
match fixing and corruption in Eastern Europe. More...
Rien ne va plus at FIFA. The news that FIFA’s Secretary General Jérôme Valcke
was put on leave and released from his
duties has been quickly overtaken by the opening of a criminal investigation targeting
both Blatter and Platini.
With FIFA hopping from one scandal to the next, one
tends to disregard the fact that it has been attempting (or rather pretending) to
improve the governance of the organisation for some years now. In previous
blogs (here and here), we
discussed the so-called ‘FIFA Governance Reform Project’, a project carried out
by the Independent Governance Committee (IGC) under the leadership of Prof. Dr.
Mark Pieth of the Basel Institute on Governance. Their third and final report, published
on 22 April 2014, listed a set of achievements made by FIFA in the area of good
governance since 2011, such as establishing an Audit and Compliance Committee (A&C).
However, the report also indicated the reform proposals that FIFA had not met.
These proposals included the introduction of term limits for specific FIFA
officials (e.g. the President) as well as introducing an integrity review
procedure for all the members of the Executive Committee (ExCo) and the
Standing Committees. More...
Editor's note
Piotr is an intern at the ASSER International Sports Law Centre.
Introduction
On 24 July the Court of Arbitration
for Sport (CAS) issued its decision in the proceedings brought by the Indian
athlete Ms. Dutee Chand against the Athletics Federation of India (AFI) and the
International Association of Athletics Federations (IAAF) in which she
challenged the validity of the IAAF Regulations Governing Eligibility of
Female with Hyperandrogenism to Compete in Women’s Competition (Regulations). The Regulations were
established in 2011 as a response to the controversies surrounding South
African athlete Caster Semenya (see e.g.
here, here, and here), and for the purpose of
safeguarding fairness in sport by prohibiting women with hyperandrogenism, i.e. those with excessive levels of
endogenous (naturally occurring) testosterone, from competing in women athletics
competitions. Owing to the subject-matter that the Regulations cover, the case
before the CAS generated complex legal, scientific and ethical questions. The
following case note thus aims at explaining how the Panel addressed the issues
raised by the Indian athlete. It follows a previous blog we published in December 2014 that
analysed the arguments raised in favour of Ms. Chand. More...
Editor's note: James Kitching is Legal Counsel and Secretary to the AFC judicial bodies at the Asian Football Confederation. James is an Australian and Italian citizen and one of the few Australians working in international sports law. He is admitted as barrister and solicitor in the Supreme Court of South Australia. James graduated from the International Master in the Management, Law, and Humanities of Sport offered by the Centre International d'Etude du Sport in July 2012.
Introduction
On 12 May 2015, the Court of Arbitration for Sport (CAS) announced that the World
Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) had filed
an appeal against the decision issued by the Australian Football League (AFL) Anti-Doping Tribunal (AADT) that thirty-four current and
former players of Essendon Football Club (Essendon)
had not committed any anti-doping rule violation (ADRV) identified within the AFL Anti-Doping Code (AADC). The players had each been charged with using
Thymosin-Beta 4 (TB4) during the
2012 AFL season.
On 1 June 2015, WADA announced that it had filed an appeal against the decision by the AADT to clear Mr.
Stephen Dank (Dank), a sports
scientist employed at Essendon during the relevant period, of twenty-one
charges of violating the AADC. Dank was, however, found guilty of ten charges and banned for life.
This blog will solely discuss the likelihood of the
first AADT decision (the Decision)
being overturned by the CAS. It will briefly summarise the facts, discuss the
applicable rules and decision of the AADT, review similar cases involving ‘non-analytical
positive’ ADRVs relating to the use of a prohibited substance or a prohibited
method, and examine whether the Code of Sports-related Arbitration (CAS Code) is able to assist WADA in its
appeal.
This blog will not examine the soap opera that was
the two years leading-up to the Decision. Readers seeking a comprehensive
factual background should view the excellent up-to-date timeline published by the
Australian Broadcasting Corporation. More...
Star Lawyer Jean-Louis Dupont is almost
a monopolist as far as high profile EU law and football cases are concerned.
This year, besides a mediatised challenge against UEFA’s FFP regulations, he
is going after FIFA’s TPO ban on behalf of the Spanish and
Portuguese leagues
in front of the EU Commission, but also before the Brussels First Instance
Court defending the infamous Malta-based football
investment firm Doyen Sport. FIFA and UEFA’s archenemy,
probably electrified by the 20 years of the Bosman ruling, is emphatically trying to
reproduce his world-famous legal prowess. Despite a first spark at a success in
the FFP case against UEFA with the Court of first instance of Brussels sending
a preliminary reference to the Court of Justice of the EU (CJEU), this has
proven to be a mirage as the CJEU refused, as foretold, to answer the questions of the Brussels Court,
while the provisory measures ordered by the judge have been suspended due to
UEFA’s appeal. But, there was still hope, the case against FIFA’s TPO ban, also
involving UEFA and the Belgium federation, was pending in front of the same
Brussels Court of First Instance, which had proven to be very willing to block UEFA’s
FFP regulations. Yet, the final ruling is another disappointment for Dupont
(and good news for FIFA). The Court refused to give way to Doyen’s
demands for provisional measures and a preliminary reference. The likelihood of
a timely Bosman bis repetita is
fading away. Fortunately, we got hold of the judgment of the Brussels court and
it is certainly of interest to all those eagerly awaiting to know whether
FIFA’s TPO ban will be deemed compatible or not with EU law. More...