Editor’s note:
Thomas Terraz is a fourth year LL.B. candidate at the International and
European Law programme at The Hague University of Applied Sciences with a specialisation
in European Law. Currently he is pursuing an internship at the T.M.C. Asser
Institute with a focus on International and European Sports Law.
1. Introduction
The UCI may soon have to navigate treacherous legal
waters after being the subject of two competition law based complaints (see here and here) to the European Commission in less than a month over rule changes and
decisions made over the past year. One of these complaints stems from Velon, a private
limited company owned by 11 out of the
18 World Tour Teams,[1]
and the other comes from the Lega del Ciclismo Professionistico, an entity
based in Italy representing an amalgamation of stakeholders in Italian
professional cycling. While each of the complaints differ on the actual
substance, the essence is the same: both are challenging the way the UCI exercises
its regulatory power over cycling because of a growing sense
that the UCI is impeding the development of cycling as a sport. Albeit in different ways: Velon sees the UCI infringing on its ability
to introduce new race structures and technologies; the Lega del Ciclismo
Professionistico believes the UCI is cutting opportunities for
semi-professional cycling teams, the middle ground between the World Tour Teams
and the amateur teams.
While some of the details remain vague, this blog
will aim to unpack part of the claims made by Velon in light of previous case
law from both the European Commission and the Court of Justice of the European
Union (CJEU) to give a preliminary overview of the main legal issues at stake
and some of the potential outcomes of the complaint. First, it will be crucial
to understand just who/what Velon is before analyzing the substance of Velon’s
complaint.
2. Who / What is Velon?
From
an outsider’s point of view, the answer to this question is not so obvious as
it may seem. Velon itself is owned by 11 World Tour Teams, which is the pinnacle
of the UCI’s men’s team classification. In other words, Velon represents more
than half of the largest team stakeholders in road cycling.[2] However, Velon does not
just simply advocate for these teams’ interests, but it engages in its own
economic activities, which can be categorized into two types. First, it has been
the organizer of a new series of races called the Hammer Series (or as the UCI
would prefer, simply Hammer) where instead of having individual cyclists
(competing on behalf of a team) placing individually in a stage of a race, the
entire team is classified through a points-based system. The point of this
format is ‘crowning the best team in professional cycling’.
Velon
also created a ‘digital content and live data platform’ through VelonLive via a
partnership with EY, which was first
made public in May of this year. VelonLive essentially collects data from road
cycling races in order to give spectators more insight into the race. For
example, it collects ‘real-time biometric rider data’, including heart rate, power and cadence data from
specific riders in a race to on bike cameras and cameras in team
cars. The aim is to try to bring the race closer to the spectator by offering
more data and new ways to see and understand the race. Major race organizers,
like the Giro D’Italia and the Tour of Flanders have jumped on these new race
visualization technologies and used VelonLive this year in their respective
races.
So
not only does Velon act as a representative of a large group of first-rate road
cycling teams, but it also organizes races and is working to develop innovative
ways for cycling fans to experience road cycling races.
3. The Complaint
Velon,
through a press release on their website, announced that it
had launched a formal complaint against the UCI to the European Commission on 20
September, 2019 to which it added an ‘Addendum to the Complaint’ on 8 November, 2019.
While these press releases and accompanied ‘context notes’ are rather bare in
explaining the factual background to the complaint, it is still enough to
extract the essence of what is being alleged. At its core, Velon is making a three-pronged
complaint against the UCI: first, that the UCI acted in a way that has
‘hampered the development of the Series’ (Hammer Series); secondly, that the
UCI is discriminating against women’s cycling by denying the approval of a
women’s race that would accompany the already existing men’s race in Hammer
Stavanger; lastly, that the amendments to the UCI’s Technical Regulations effectively
take away Velon and other race organizers’ control over live race data technologies
and were adopted without sufficiently consulting stakeholders. Concerning the last complaint, Velon
seems to be referring to certain amendments from 15 February, 2019 made to the equipment regulations Article 1.3.024ter.
The changes essentially introduced a pre-authorization scheme
for ‘onboard technology equipment’ in which the UCI or an event organizer with the
UCI’s consent must give prior authorization for ‘any intended use by a team or
rider’ of such equipment. However, given both the scarce details and length
restraints, this
blog concentrates on the on the first two elements of the complaint, which are
further dissected here.
Velon
alleges that the UCI acted to prevent the organization of Hammer races into a series
and threatened to not register the men’s Hammer races in the 2020 calendar if Velon
proceeded to do so. As of 11 November, 2019, the three men’s Hammer
races are still listed in the 2020 calendar, while the women’s
Hammer Stavanger race is not listed, since it was rejected by the UCI. Velon also claims
that the UCI did not give any reasons for its opposition to the series and that
it ‘hampered’ the overall development of the series. Further details are rather
murky; however, it is essential to point out that the UCI, like many other
SGBs, employs a pre-authorization scheme[3] for cycling events, and it
prohibits both teams and individual cyclists (of all levels) in participating
in non-authorized third-party events under the threat of sanctions. Individuals
may face a one-month suspension and a fine of 50 to 100 CHF.[4] Such an event
pre-authorization scheme has been the focal point of two major EU sports
competition law cases: the CJEU’s decision in MOTOE and the Commission’s decision concerning the ISU’s
eligibility rules. It is likely that if the Commission takes on this case, it
will closely scrutinize the UCI’s pre-authorization scheme and its actual
application, including the accompanied sanctions. From the outset, it is
critical to bear in mind that the CJEU has held that rules of sport governing
bodies may escape the prohibitions under Article 101 TFEU if ‘the consequential effects restrictive of
competition are inherent in the pursuit of those objectives (Wouters
and Others, paragraph 97) and are proportionate to them’.[5] On the other hand, a
dominant undertaking may justify its actions under Article 102 TFEU if it can
demonstrate ‘that its conduct is objectively necessary or by demonstrating that
its conduct produces substantial efficiencies which outweigh any
anti-competitive effects on consumers’.[6]
As
a preliminary note, it should be stated that if the Commission decides to pursue
the case under Article 102 TFEU, it will not be hard pressed to find the UCI and
its respective national federations collectively dominant[7] in the relevant market.[8]
The relevant market regarding the Hammer races will most likely be confined to
the organization and commercial exploitation of international road cycling
races on the worldwide market.[9]
Even though the Professional Cycling Council (PCC) adopts the UCI WorldTour
calendar, Velon could still contend that the UCI exerts control over its
adoption given the composition of the PCC.[10]
4. Analysis of the ‘hampered’ Series and alleged discrimination
against women’s cycling
4.1.MOTOE
In
MOTOE, ELPA, a Greek motorsport
organization, was given the regulatory power through a national law to approve
or deny motorsport events in Greece, while also organizing and commercially
exploiting such events itself.[11] MOTOE challenged the
national law giving ELPA this power after one of its events was not approved. The
CJEU ruled that the dual role of ELPA as both a regulator and commercial
exploiter was contrary to competition law because it had not given an ‘equality
of opportunity’ ‘between the various economic operators’.[12] AG Kokott’s Opinion goes
further and describes a ‘conflict of interest’ in which sport governing bodies are
placed if they are both the gatekeeper and promoter of sport events.[13] A similar situation in
the Commission’s FIA case even resulted in the complete separation of FIA’s
‘commercial and regulatory functions’ in order to cease its breach of EU
competition law.[14]
Unlike
ELPA, the UCI is not given the power to regulate the events included in its
calendar by an act of a state or public body. Nonetheless, it still wields an
immense power over the regulation and approval of events in road cycling deriving
from its position as the world’s
cycling governing body. The UCI also benefits considerably from the
registration of events in its calendar, a fact that is quickly verified by
having a glance at its yearly financial report,[15] which demonstrates the
extent to which it is dependent on revenues connected to its sanctioned events.
The UCI can only justify charging fees for events if there is the existence of
an official closed calendar of events. Additionally, the UCI itself is an event
organizer since it arranges the annual UCI Road World Championships. Therefore,
it is very likely that the UCI may be faced with a ‘conflict of interest’ because
it holds the keys to its events calendar while having an apparent financial stake
in the approval of events.
At this
point, it is also helpful to examine the Commission’s decision in the ISU case which
delves in depth on the compatibility of event pre-authorization schemes with EU
law.
4.2.The Commission’s ISU
Decision
The ISU case concerned two Dutch speed skaters who
challenged the ISU eligibility rules precluding them from participating in
non-ISU authorized events, subject to a potential lifetime ban (the ban was
amended during the proceedings to allow greater flexibility on the sanction but
was still found to be contrary to EU law). The concerned skaters wished to participate
in IceDerby’s events. IceDerby is an ice-skating events organizer who aimed to
create a new race format that would introduce ‘a new type of skating events on
a different size track than the ISU recognized track’.[16] This
very much echoes some of the fact pattern of the present case in which Hammer
seeks to introduce a new road cycling race format. The Commission found that
the severity of the sanctions in case of a breach of the ISU’s eligibility
rules inherently aimed ‘at preventing athletes from participating in events not
authorised by the ISU, resulting in the foreclosure of competing event
organizers’.[17] In the end, the case
largely turned on whether the ISU’s eligibility rules pursued legitimate
objectives and whether they were inherent and proportionate to its aims. The
Commission identified that ‘the integrity of the sport, the protection of the
athletes’ health and safety and the organisation and proper conduct of sport’
could be considered legitimate objectives but that the ISU’s eligibility rules
did not actually pursue any of these objectives.[18] Moreover,
the Commission found that the financial and economic interests of the ISU could
not be considered legitimate objectives.[19]
In Velon’s complaint, as in the ISU case, there are
two connected, yet separate elements that the Commission will most likely have
to analyze: (a) the prohibition of participating in non-approved events and the
relevant sanctioning framework and (b) the UCI’s events approval process (the pre-authorization
scheme). Concerning the former, Pat McQuaid, the former UCI president explained
the aim of the rules banning participation in non-approved events in a letter to USA
Cycling back in 2013. He explained that it ‘allows for a
federative structure’, ‘which is inherent in organised sport and which is
essential to being a part of the Olympic movement’. The Commission dismissed
this notion in the ISU case when it pointed out that there are several sport
federations that do not have an ‘ex-ante control
system’ that effectively precludes athletes from participating in third party
events.[20] Nevertheless,
this stated objective may still fall under the organization and proper function
of sport, which was deemed a legitimate objective by the Commission.
However, the issue remains as to whether the UCI’s pre-authorization
scheme, the latter element identified above, pursues legitimate objectives
while meeting the proportionality requirements. In other words, why does the UCI oppose the
organization of Hammer races in a series and approving a corresponding women’s
event? From Velon’s claims, it is questionable whether the UCI has a ‘pre-established
objective, nondiscriminatory and proportionate criteria’ in approving events since
it claims that it never received an explanation as to why its series was
rejected.[21] In addition, the UCI must elaborate
its reasoning in denying a women’s Hammer Stavanger event beyond that it ‘was
not in the best interest of women’s cycling’. The UCI will have to explain why
it not only allegedly threatened to remove Hammer races from the calendar and
denied the inclusion of a women’s race but also why it did not provide Velon a full
response that gave objective justifications, not tied to any economic or
financial interests, as to why it is opposed the organization of a Hammer
Series and a women’s Hammer Stavanger race.
In the end, in order for the ISU to keep its event
pre-authorization scheme it was required to: (a) ‘provide for sanctions and authorization
criteria that are inherent in the pursuit of legitimate objectives’, (b)
‘provide for objective, transparent and non-discriminatory sanctions and
authorization criteria’ that are proportionate to its objectives, and (c) ‘provide
for an objective, transparent and non-discriminatory procedure for the adoption
and effective review of decisions’ concerning the ‘authorisation of speed
skating events’.[22] The Commission will likely
evaluate the UCI’s pre-authorization scheme in light of these criteria.
4.2.1. The UCI’s
pre-authorisation scheme in light of the ISU criteria
This examination will begin by investigating the
second and third criteria before returning to the first criteria. On the second
criteria, the UCI lays out the sanctions for participating in ‘forbidden races’
in Part 1 of its Regulations under Article 1.2.021 that plainly states that
breaches ‘shall render the licence holder liable to one month’s suspension and
a fine of CHF 50 to 100’. Since the sanction is not nearly as draconian as the
ISU’s sanctions, the UCI may have a greater chance of arguing that it is
proportionate to its objective, although it could still be argued that the
sanction does not give much flexibility depending on the circumstances of the
case.[23]
Concerning the event authorization criteria, the UCI explains the requirements
to register a race in the international calendar in the ‘Registration Procedure
for UCI Calendars 2020/2020-2021’, which sets out
the financial obligations of event organizers, the relevant deadlines, and the documentation[24] that
event organizers will have to provide. In addition, the UCI does not have the
same intrusive financial disclosure requirements, which was strongly rebuked by
the Commission.[25] However, nowhere does it explicitly
mention ‘an interest of cycling’ criteria, which makes it a real wonder as to
why this was the reason given, according to Velon, concerning the rejection of the
women’s Hammer Stavanger race. Consequently, the Commission will have to
examine whether the criteria are in practice applied in a uniform and
non-discriminatory manner and whether the UCI uses other criteria to assess the
inclusion of an event on the international calendar. The Commission did not condone
the ISU’s non-exhaustive list of criteria and the broad margin of discretion it
had in approving or rejecting event applications.[26]
On the third criteria, the UCI does have a rather transparent
process (see flow chart below[27])
concerning the adoption of its calendar, and it also has a process for the
review of a rejection of an event application.[28] If
the UCI management committee rejects an application, the event organizers may
have the opportunity to defend the application. If it does not have this
opportunity, the organizer may appeal to the UCI’s arbitral board, however, the
decision is final and cannot be appealed further. It is at this point that the
UCI’s event pre-authorization scheme may run into further difficulties meeting
the ISU criteria because it does not even allow the possibility for the
organizer to appeal to the CAS. Even the ISU in its Communication No.
1974 allowed for an appeal to the CAS, which still did
not preclude the Commission from questioning the extent an appeals arbitration
would ensure the effectiveness of EU competition law, to which it concluded
that an appeal to the CAS reinforced the restriction of competition.[29] Against
this background, the Commission would likely find the UCI’s grip over the
review process restrictive of competition.
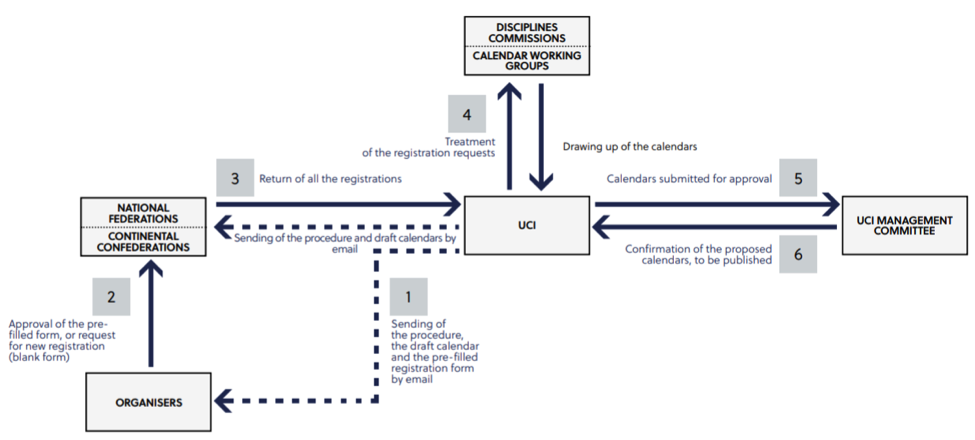
Returning to the first of the ISU criteria, the
question is whether the UCI’s sanctions and pre-authorization criteria are
inherent in the pursuit of a legitimate objective. Considering the above, it is
doubtful whether the potentially open list of criteria and the limited
effective review of decisions could be considered inherent in the pursuit of a
legitimate objective such as ‘the organisation and proper conduct of sport’. Furthermore,
Velon’s case may turn on how well it can demonstrate that it has been unjustly
put under pressure from the UCI.
4.3. Final thoughts on
the ‘hampered’ series
It appears that the UCI has allegedly wielded its
regulatory power through its event pre-authorization scheme to force Velon to
remove a critical aspect of its races: the series. The UCI’s alleged move is
further puzzling by the fact that none of the Hammer races interfere with the men’s
or women’s World Tour race calendar (with the exception of Il Lombardia and
Hammer Hong Kong), meaning that teams and riders would anyway be available. Even
if there was an interference, it is important to keep in mind that professional cycling teams are usually sufficiently
large and organized to compete in more than one race in the world
simultaneously.
Finally, while the UCI did not actually remove the men’s Hammer races from
the
calendar, just an imminent threat of
doing so may be sufficient to restrict competition. Cyclists are severely discouraged to
participate in non-authorized events considering the sanctions they may face.
Hence, event organizers, such as Velon, are completely reliant on the UCI to
approve their events in order to have any chance at a successful and economically viable event,[30] and consequently, Velon cannot risk losing the UCI’s
approval for the Hammer races. Furthermore,
the UCI has in practice already denied a women’s race at Hammer Stavanger,
which greatly strengthens Velon’s claims against the UCI. Lastly, given the vagueness
of the claim that the UCI overall hampered the development of the Hammer
Series, it is possible that there are additional details that have not been
publicized that could further support a potential violation of EU competition
law by the UCI.
5. Conclusion
Velon has also requested interim measures that would
force the UCI’s approval of a women’s race during Hammer Stavanger 2020. However, since interim
measures are rarely granted,[31] it is unlikely Velon will succeed
on this front. Nevertheless, based on the discussion above, there are quite a
few signs that the UCI has perhaps overstepped its regulatory powers. The UCI’s
alleged actions, especially its opposition to the organization of a women’s
Hammer Stavanger race, beg the question as to how it will defend its decision as
pursuing legitimate objectives and respecting the proportionality requirements.
Moreover, it should be recalled that Velon’s complaints also concern the UCI’s
equipment regulations and that there is a completely separate complaint from the Lega del Ciclismo Professionistico. Thus, due to the
large territorial scope and the potentially wide range of actors affected by
the UCI’s actions in these cases, it would be a missed opportunity if the
Commission declines to further elucidate how sport governing bodies must exercise
their regulatory powers in order to comply with EU competition law, especially
when their own financial interests may be in play.