2015 was a good year for
international sports law. It started early in January with the Pechstein
ruling, THE
defining sports law case of the year (and probably in years to come) and ended
in an apotheosis with the decisions rendered by the FIFA Ethics
Committee against Blatter and Platini. This blog will walk you through the
important sports law developments of the year and make sure that you did not
miss any.
The Court of
Arbitration for Sport challenged by German Courts
The more discrete SV Wilhelmshaven ruling came
first. It was not even decided in 2015, as the ruling was handed out on 30
December 2014. Yet, unless you are a sports law freak, you will not have taken
notice of this case before 2015 (and our blog). It is not as well known as the Pechstein ruling, but it is challenging
the whole private enforcement system put in place by FIFA (and similar systems
existing in other SGBs). Indeed, the ruling foresees that before enforcing a
sanction rendered by FIFA, the national (or in that case regional) federation
must verify that the award underlying the sanction is compatible with EU law.
The decision has been appealed to the Bundesgerichtshof (BGH) and a final
ruling is expected in 2016.
Later on, in January, the
Oberlandesgericht München dropped its legal bomb in the Pechstein case. The court refused to recognize the CAS award
sanctioning Claudia Pechstein with a doping ban, as it was deemed contrary to
German antitrust rules. The reasoning used in the ruling was indirectly
challenging the independence of the CAS and, if confirmed by the BGH, will trigger
a necessary reform of the functioning and institutional structure
of the CAS. Paradoxically, this is a giant step forward for international
sports law and the CAS. The court acknowledges the need for CAS arbitration in
global sport. However, justice must be delivered in a fair fashion and the
legitimacy of the CAS (which relies on its independence from the Sports
Governing Bodies) must be ensured (see our long article on the case here).
We will see how the BGH will deal
with these cases in 2016. In any event, they constitute an important warning
shot for the CAS. In short, the CAS needs to take EU law and itself seriously.
If it truly addresses these challenges, it will come out way stronger.
The new World
Anti-Doping Code and the Russian Doping Scandal
On the doping front, 2015 is the
year in which the new World Anti-Doping Code (WADC) came into force (see our Blog Symposium). The Code introduces substantial
changes in the way the anti-doping fight is led and modifies the sanction regime applicable in case of an adverse
analytical finding. It is too early to predict with certainty its effects on
doping prevalence in international sports. For international sports lawyers,
however, it is in any event a fundamental change to the rules applicable to anti-doping
disputes, which they need to get closely acquainted with.
The new World Anti-Doping Code was
largely overshadowed by the massive doping scandal involving Russian sports,
which was unleashed by an ARD documentary (first released in 2014) and revived
by the crushing report of the Independent Commission
mandated by the World Anti-Doping Agency to investigate the matter. This
scandal has shaken the legitimacy of both the anti-doping system and the International Association of Athletics
Federations (IAAF). It has highlighted the systematic shortcomings of
the anti-doping institutions in Russia, and, the weakness of the control
exercised on these institutions at a transnational level, be it by IAAF or
WADA.
In 2015 again, doping proved to be a
scourge intimately linked with international sports. The confidence and the
trust of the public, and of clean athletes, in fair sports competitions is anew
put to the test. WADA, which was created in the wake of another massive doping
scandal in the nineties, has shown its limits. In practice, the
decentralization of the enforcement of the WADC empowers local actors, who are
very difficult to control for WADA. Some decide to crackdown on Doping with
criminal sanctions (see the new German law adopted in December 2015), others
prefer to collaborate with their national athletes to improve their
performances. The recent proposals at the IOC level aiming at shifting
the testing to WADA can be perceived as a preliminary response to this problem.
Yet, doing so would entail huge practical difficulties and financial costs.
EU law and sport: 20
years of Bosman and beyond
2015 was also the year in which the
twentieth anniversary of Bosman was
commemorated through multiple conferences and other sports law events. The
ASSER International Sports Law Centre edited a special edition of the Maastricht Journal of European
and Comparative Law and a book celebrating the legacy of the ruling is
forthcoming with the publisher Springer. The ruling did not have the dramatic
effects predicted at the time of the decision, since football is still alive
and kicking. Surely, it has given way to new challenges and sharply accelerated
the transnationalization of football (and sport in general). A key legacy of Bosman is that this
transnationalization, which goes hand in hand with the commercialization of
sport, cannot side-line an essential category of stakeholders: the athletes.
It is with this spirit in mind, and
a little push of the ASSER International Sports Law Centre, that the European Commission
decided to open an investigation into the rules of the International
Skating Union (ISU) barring, under the threat of a life ban, speed skaters (and
any other affiliate) from joining speed skating competitions which are not
condoned by the ISU. Though the case is rather low profile outside of the
Netherlands, this is an important step forward for the EU Commission, as it had
not opened an EU competition law investigation in sporting matters in almost 15
years. Many other competition law complaints (e.g. TPO or Formula 1) involving sport are currently pending in
front of the EU Commission, but it is still to decide whether it will open a
formal investigation. 2015 is also the year in which we have desperately expected the release of the EU State aid
decisions regarding football clubs, and amongst them Real Madrid, but in the
end this will be a matter for 2016.
FIFA and the chaotic
end of the Blatter reign
FIFA is not the only SGB to have put
an abrupt end to the (very) long reign of its great leader (think of the messy
downfall of Diack at the IAAF). Yet, when talking about FIFA and
football, the resonance of a governance crisis goes well beyond any other. It
is truly a global problem, discussed in nearly all news outlets. This
illustrates very much how a Swiss association became a global public good, for
which an Indian, Brazilian, American or European cares as much as a Swiss, who
is in traditional legal terms the only one able to influence FIFA’s structure
through legislation. The global outrage triggered by the progressive release by
the US authorities of information documenting the corrupt behaviour of FIFA
executives has led to two immediate consequences: a change of the guard and a
first reform of the institution.
There are now very few FIFA Executive Committee members left who were
present in 2010 for the election of Qatar as host city for the 2022 World Cup.
The long-time key figures of FIFA, Blatter, Platini and Valcke, are unlikely to
make a comeback any time soon. And, the upcoming February election of the new
FIFA president is more uncertain than ever with five candidates remaining. Simultaneously, FIFA has announced some governance reforms, which aim
at enhancing the transparency of its operation and the legitimacy of its
decision-making. We are living through a marvellous time of glasnost and
perestroika at FIFA. The final destination of this transformative process remains
unknown. There are still some major hurdles to overcome (starting with the one
association/one vote system at the FIFA congress) before FIFA is truly able to
fulfil its mission in a transparent, accountable and legitimate manner. We hope
it will be for 2016!
The ASSER
International Sports Law Blog in 2015
Finally, a few words on our blog in
2015. In one year we have published 60 posts, our most-read-blog concerned the Pechstein ruling that was read 3054 times.
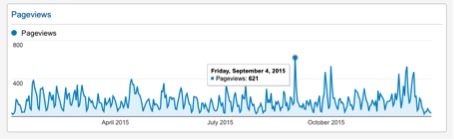
Our peak day was reached on 4
September with 621 page views (thanks to a great post on the Essendon
case by @jrvkfootball).
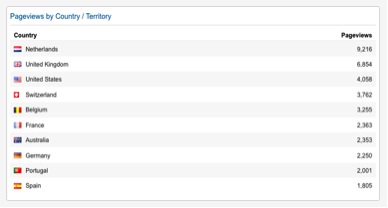
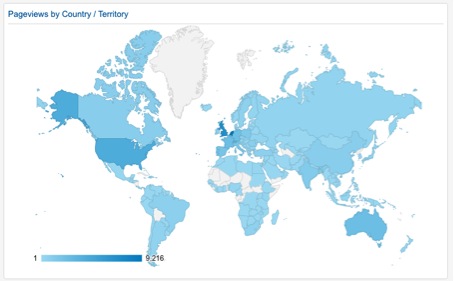
Our readers are based all around the
world, but the majority is based in the EU and the US.
We hope to
be able to keep you interested and busy in 2016 and we wish you a great year!
The ASSER
International Sports Law Blog Team