After the success of this year’s World Cup in Brazil, FIFA President
Sepp Blatter can start concentrating on his Presidential campaign for next
June’s FIFA elections. Even though the 78-year old Swiss is not officially a
candidate yet, he is still very popular in large parts of the world, and
therefore the favourite to win the race. Nonetheless, even for the highly
experienced Mr. Blatter these elections will be different. All candidates will
have to respect the newly introduced Electoral Regulations for the FIFA Presidency.
The Electoral Regulations are the latest addition to the reform process FIFA initiated more than two years ago following
the controversial awarding of the 2018 and 2022 World Cups to Russia and Qatar.
The stated aim of the Regulation is to make the elections more transparent,
democratic and to prevent possible corruption accusations.[1] Its
legal basis is found in Article 24(4) of the 2013 FIFA Statutes and reads as follows:
“The conditions to be observed
during a candidature for the office of President are stipulated in the Electoral Regulations for the FIFA
Presidency. These regulations shall be issued by the Executive Committee.”
Earlier editions of the FIFA Statutes did not include a reference to
electoral regulations. In comparing the 2013 Statutes with the 2010 Statutes
used for the previous elections one can witness the extent of this dramatic
change. Pursuant to Article 24 of the 2010 edition, “only the Members[2]
may propose candidatures for the office of FIFA President. Members shall notify
the FIFA general secretariat in writing in the name of a candidate for the FIFA
presidency at least two months before the date of the Congress.” Furthermore,
“the general secretariat shall notify the
Members of the names of proposed candidates at least one month before the date
of the Congress.” Other criteria regarding the eligibility of candidates
were not included.
The first fundamental change to take place at the 2015 election will be
the setting up of an Ad-hoc electoral Committee pursuant to Article 7(1)
Electoral Regulations. The Ad-hoc Electoral Committee shall be composed of the
chairman of the FIFA Disciplinary Committee, the chairman of the FIFA Appeal
Committee and the chairman of the FIFA Audit and Compliance Committee[3]
and shall assess whether a candidate meets the profile specifications provided
for by the eligibility criteria stipulated in Article 13 of the Electoral
Regulations and Article 24 of the FIFA Statutes.[4]
The second fundamental change is that, in accordance with article 13(1),
Candidates for the office of President must meet the following requirements:
The
candidate shall have played an active role in association football (as a board
member, committee member, referee and assistant referee, coach, trainer and any
other person responsible for technical, medical or administrative matters in
FIFA, a Confederation, Association, League or Club or as a player) for two of
the last five years before being proposed as a candidate (cf. art. 24 par. 1 of
the FIFA Statutes).
The
candidate shall have been proposed by a member association in accordance with
art. 24 par. 1 of the FIFA Statutes.
The candidate shall present declarations of
support from at least five member associations (cf. art. 24 par. 1 of the FIFA
Statutes). Being proposed as a candidate by a member association shall be
understood as a declaration of support. Each member may only present a
declaration of support for one person. If a member association presents
declarations of support for more than one person, all its declarations shall
become invalid.
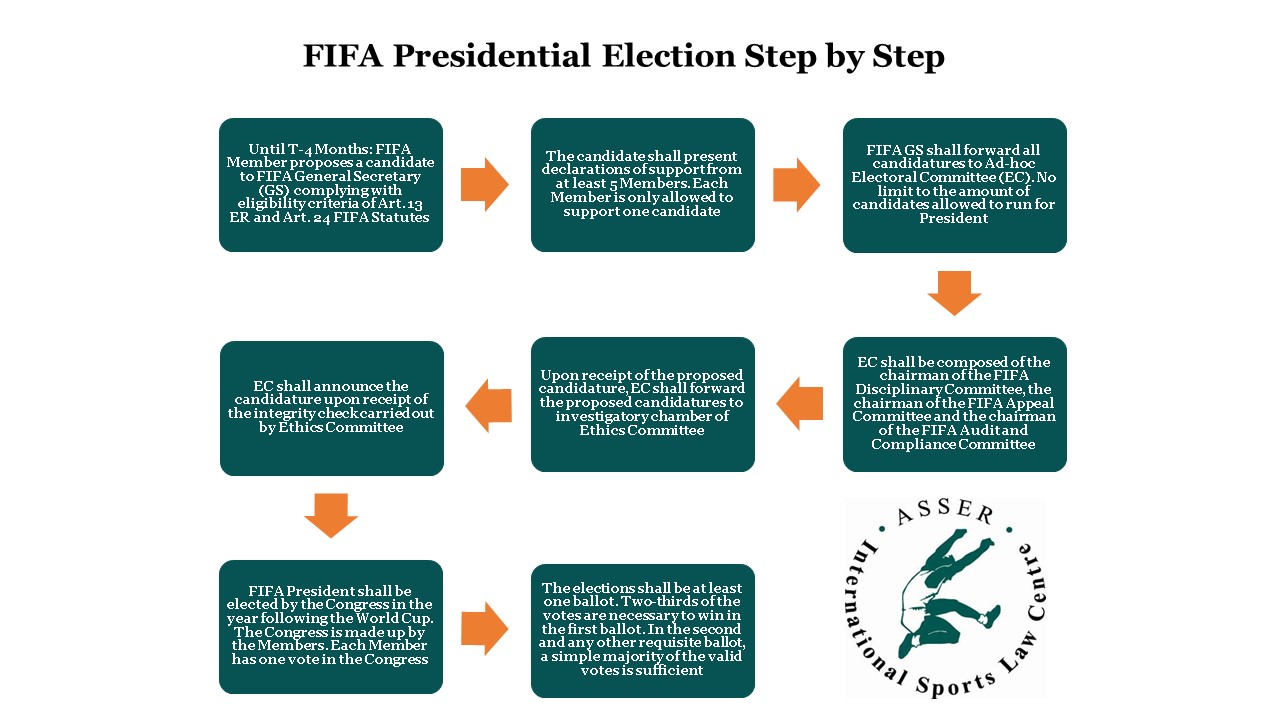
The flowchart below summarises the key procedural steps set out in the Electoral
Regulations:
Has the Presidential campaign already begun?
The Presidential campaign has already started due to the fact that one
person has declared himself a candidate. This person is neither Mr. Blatter nor
“Europe’s favourite” Michel Platini, but former FIFA official Jérôme Champagne. Mr. Champagne, who is personally funding his own campaign, has stated that he has
received the support of at least five Member Associations and that the FIFA
general secretariat has been notified of his candidature. Details on which
Member Associations support the Frenchman remain undisclosed.
During the last FIFA Congress that took place in Sao Paulo in June this
year, the Ad-Hoc Electoral Committee was also set up consisting of Mr. Domenico Scala (ltaly), chairman
of the FIFA Audit and Compliance Committee, Mr. Claudio Sulser (Switzerland),
chairman of the FIFA Disciplinary Committee, and Mr. Larry Mussenden (Bermuda),
chairman of the FIFA Appeal Committee. The next step would be for the Ad-hoc
Electoral Committee to forward the proposed candidature of Jérôme Champagne to
the Ethics Committee pursuant Article 15(10) of the Electoral Regulations.
As stated above, Sepp Blatter is not yet a candidate, but it is expected
that he will run for a fifth consecutive term in office. Interestingly enough,
in accordance with Article 2(2) of the Electoral Regulations, “if a person engages in campaign or similar
activities that give the appearance that he is a candidate, the Ad-hoc
Electoral Committee or, if the Ad-hoc Electoral Committee has not yet been
constituted, the FIFA Secretary general, shall give him a deadline of ten days
to formally state his intention of becoming a candidate. This shall also apply
for the incumbent FIFA President. Blatter hinted several times this year
that he is thinking about running for President again. Nonetheless, it appears
that the rule stipulated in Article 2(2) has not been applied to him (yet). With regard to the possible third candidate, Michel Platini has said that he is considering becoming a candidate
and promised to make a decision by the draw for the Champions League on 28
August.
Could the new Election Regulations jeopardise Mr. Blatter’s possible
re-election ambitions?
Given that Blatter still enjoys widespread support in the “football
family”, he should have no problem securing the declarations of support from
five different Members. As regards the integrity check, it is worth noting that
Sepp Blatter has never been personally accused of corruption. True, there has
been a lot of controversies at FIFA under his watch (Qatar2022 is the latest
and most acute one) and questions can be raised whether an 80-year old is the
ideal candidate to run one of the world’s most important Sporting Governing
Bodies for the next four years.
Conclusion
Whether the new Election Regulations will make next year’s election more
transparent and democratic will mostly depend on how they will be applied during
the unfolding campaign and elections. Will Blatter’s double game as a candidate
and FIFA President be closely scrutinized? On what basis and to which extent
will the Ethics Committee review the candidatures? Even if the electoral
regulations appear to have some teeth in practice, further reforms will still
be necessary to improve FIFA’s legitimacy. One can, and Jérôme Champagne has in
fact suggested it, imagine public debates between the candidates to be
broadcasted worldwide. Furthermore, one should envisage that the vote must be
held publically and that the number of terms as FIFA president must be restricted.
There is a lot to do before FIFA could be considered, as far as it is even
possible, a “democratic” organisation, but the sheer fact of having electoral
regulations is already a step in the right direction.
P.S. At the beginning of July Jérôme Champagne visited the Asser institute and presented his program for the upcoming FIFA Presidential elections 2015. The video is available at:
[1] http://www.insideworldfootball.com/fifa/15040-fifa-lays-out-rules-of-engagement-in-the-battle-for-the-presidency.
[2] Member: an Association which is
responsible for organising and supervising football in all of its forms in its
Country that has been admitted into membership of FIFA by the Congress.
[3] Electoral Regulations for the FIFA Presidency, Article
7(2)
[4] Electoral Regulations for the FIFA Presidency, Article
8(1)d)