On Thursday 25 February 2021 from 16.00-17.30 CET, the Asser International Sports Law Centre, in collaboration with Dr Marjolaine Viret (University of Lausanne), organizes a Zoom In webinar
on the recent award of the Court of Arbitration for Sport (CAS) in the
case World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) v. Russian Anti-Doping Agency
(RUSADA), delivered on 17 December 2020.
Background
In its 186 pages decision
the CAS concluded that RUSADA was non-compliant with the World
Anti-Doping Code (WADC) in connection with its failure to procure the
delivery of the authentic LIMS data (Laboratory Information Management
System) and underlying analytical data of the former Moscow Laboratory
to WADA. However, the CAS panel did not endorse the entire range of
measures sought by WADA to sanction this non-compliance. It also reduced
the time frame of their application from four to two years. The award
has been subjected to a lot of public attention and criticisms, and some
have expressed the view that Russia benefited from a lenient
treatment.
This edition of our Zoom in webinars will focus on assessing the
impact of the award on the world anti-doping system. More specifically,
we will touch upon the decision’s effect on the capacity of WADA to
police institutionalized doping systems put in place by certain states,
the ruling’s regard for the rights of athletes (Russian or not), and its
effect on the credibility of the world anti-doping system in the eyes
of the general public.
To discuss the case with us, we are very happy to welcome the following speakers:
Participation is free, register HERE.
In 2009, Sepp
Blatter expressed his concerns that half of the
players participating in the 2014 FIFA World Cup would be Brazilians naturalized
by other countries. The Official list of Players released a few weeks ago tends to prove him
wrong[1].
However, some players have changed their eligibility in the past and will even be
playing against their own country of origin[2].
This post aims at explaining the key legal aspects in changes of national
affiliation and to discuss the regulations pertaining to the constitution of
national sides in general[3]. More...
Our first report on the FIFA business dealt with FIFA’s revenues and highlighted
their impressive rise and progressive diversification. In parallel to this
growth of FIFA’s income, it is quite natural that its expenses have been
following a similar path (see Graph 1). However, as we will see FIFA makes it
sometimes very difficult to identify precisely where the money is going. Nonetheless,
this is precisely what we wish to tackle in this post, and to do so we
will rely on the FIFA Financial reports over the last 10 years.
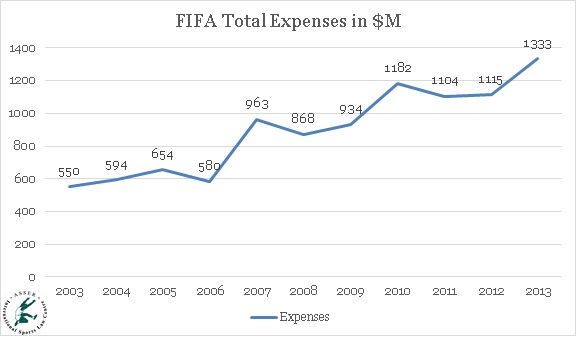
Graph 1: FIFA Expenses in USD million (adjusted for inflation),
2003-2013.
More...
After a decade of financial misery,
it appears that Valencia CF’s problems are finally over. The foreign takeover by
Singaporean billionaire Peter Lim will be concluded in the upcoming weeks, and
the construction on the new stadium will resume after five years on hold due to
a lack of money. On 3 June Bankia, the Spanish bank that “saved” Valencia CF in
2009 by providing a loan of €81 million, gave the green light for the takeover. However, appearances can be
deceiving.More...
In
April 2014, the Swedish Gambling Authority (Lotteriinspektionen) warned the
organisers of the Stockholm
Marathon that it would impose a fine of SEK 2
million (ca. € 221.000) for its sponsorship agreement with online betting
operator Unibet. The Authority found that the sponsorship agreement violates
§38 of the Swedish Lotteries Act, which prohibits the promotion of gambling
services that are not authorized in Sweden.[1] The
organisers, however, refused to withdraw Unibet as its sponsor and prominently
displayed the Unibet logo at the event, which took place on 31 May 2014. As a
result, the organisers of the Stockholm Marathon now face legal action before
the Swedish administrative courts. More...
On next Thursday the 2014 World
Cup will kick off in Sao Paulo. But next week will also see the FIFA members meeting on Tuesday and Wednesday at a
much awaited FIFA congress. For this special occasion we decided to review
FIFA’s financial
reports over the
last ten years. This post is the first of two, analysing the reports and
highlighting the main economic trends at play at FIFA. First, we will study the
revenue streams and their evolution along the 2003-2013 time span. In order to ensure
an accurate comparison, we have adjusted the revenues to inflation, in order to
provide a level playing field easing the comparative analysis over the years
and types of revenues. Our first two graphs gather the main revenue streams
into two comparative overviews. Graph 1 brings together the different types of
revenues in absolute numbers, while Graph 2 lays down the share of each type of
revenues for any given year (the others category covers a bundle of minor
revenue streams not directly relevant to our analysis).
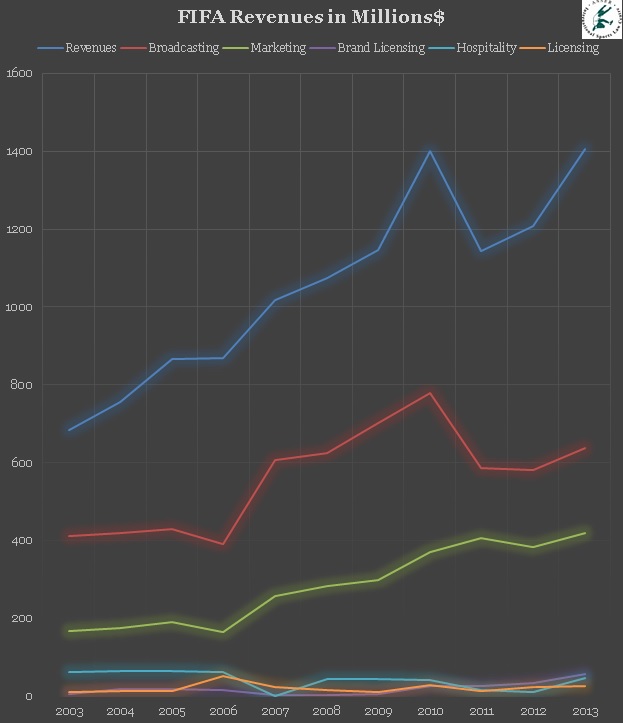
Graph 1: FIFA revenues
in Millions of Dollars, 2003-2013 (adjusted for iy Rhys Lenarduzzi
Editor’s note: Rhys Lenarduzzi recently
completed a Bachelor of Law (LL.B) and Bachelor of Philosophy (B.Phil.) at the
University of Notre Dame, Sydney, Australia. As a former professional athlete,
then international sports agent and consultant, Rhys is interested in
international sports law, policy and ethics. He is currently undertaking an
internship at the T.M.C. Asser Institute with a focus on Transnational Sports
Law.
As one may have gathered from the series
thus far, the question that comes out of this endeavour for me, is whether
redistribution in football would be better divorced from the transfer system?
In my introductory
blog I point towards historical,
cultural, and of course the legal explanations as to why redistribution was
established, and why it might be held onto despite obvious flaws. In my second
blog, I point out how the training
compensation and solidarity mechanisms work in practice through an African case
study, as well as the hindrance caused and the Eurocentricity of the
regulations. The key take-away from my third
blog on the non-application of training
compensation in women’s football might be that training compensation should
apply to both men’s and women’s football, or neither. The sweeping
generalisation that men’s and women’s football are different as justification for
the non-application to the women’s game is not palatable, given inter alia
the difference between the richest and poorest clubs in men’s football. Nor is
it palatable that the training compensation mechanism is justified in men’s
football to incentivise training, yet not in women’s football.
In the fourth
blog of this series, I raise concerns that
the establishment of the Clearing House prolongs the arrival of a preferable
alternative system. The feature of this final blog is to consider alternatives
to the current systems. This endeavour is manifestly two-fold; firstly, are
there alternatives? Secondly, are they better? More...
Editor’s note: Rhys Lenarduzzi recently completed a Bachelor of Law (LL.B) and a Bachelor of Philosophy (B.Phil.) at the University of Notre Dame, Sydney, Australia. As a former professional athlete, then international sports agent and consultant, Rhys is interested in international sports law, policy and ethics. He is currently undertaking an internship at the T.M.C. Asser Institute with a focus on Transnational Sports Law.
In September 2018, the Football Stakeholders Committee endorsed the idea of a Clearing House that was subsequently approved in October of the same year by the FIFA Council. A tender process commenced in July 2019 for bidders to propose jurisdiction, operation and establishment. Whilst many questions go unanswered, it is clear that the Clearing House will be aimed at closing the significant gap between what is owed and what is actually paid, in respect to training compensation and solidarity payments. The Clearing House will have other functions, perhaps in regard to agents’ fees and other transfer related business, though those other operations are for another blog. It will hence act as an intermediary of sorts, receiving funds from a signing and therefore owing club (“new” club) and then moving that money on to training clubs. Whilst separate to FIFA, to what extent is unclear.
I have landed at the position of it being important to include a section in this blog series on the soon to commence Clearing House, given it appears to be FIFA’s (perhaps main) attempt to improve the training compensation and solidarity mechanisms. As will be expanded upon below, I fear it will create more issues than it will solve. Perhaps one should remain patient and optimistic until it is in operation, and one should be charitable in that there will undoubtedly be teething problems. However, it is of course not just the function of the Clearing House that is of interest, but also what moving forward with the project of the Clearing House represents and leaves unaddressed, namely, the issues I have identified in this blog series. More...
On Wednesday 20 January 2021 from 16.00-17.30 CET, the Asser International Sports Law Centre, in collaboration with Dr Marjolaine Viret, is organising a Zoom In webinar
on the recent judgment of the General Court in the case International
Skating Union (ISU) v European Commission, delivered on 16 December
2016. The Court ruled on an appeal against the first-ever antitrust
prohibition decision on sporting rules adopted by the European
Commission. More specifically, the case concerned the ISU’s eligibility
rules, which were prohibiting speed skaters from competing in
non-recognised events and threatened them with lifelong bans if they did
(for more details on the origin of the case see this blog).
The ruling of the General Court, which endorsed the majority of the
European Commission’s findings, could have transformative implications
for the structure of sports governance in the EU (and beyond).
We have the pleasure to welcome three renowned experts in EU
competition law and sport to analyse with us the wider consequences of
this judgment.
Guest speakers:
Moderators:
Registration HERE
Zoom In webinar series
In December 2020, The Asser International Sports Law Centre in collaboration with Dr Marjolaine Viret launched a new series of zoom webinars on transnational sports law: Zoom In. You can watch
the video recording of our first discussion on the arbitral award
delivered by the Court of Arbitration for Sport (CAS) in the Blake
Leeper v. International Association of Athletics Federations (IAAF) case
on the Asser Institute’s Youtube Channel. Click here to learn more about the Zoom In webinar series.